As Jeff Bezos from Amazon says, “We see our customers as invited guests to a party, and we are the hosts.”
Knowing how customers behave is now essential for businesses, not a bonus. A study from Mckinsey shows that companies that focus on consumer behavior do better. They outperform their competitors by 85% in sales growth and over 25% in gross margin.
Understanding consumers can help businesses tailor their offerings. It assists them in meeting their target audience’s changing desires and needs. This builds loyalty and drives growth.
In this article, you’ll learn about the types and models of consumer behavior. These models explain why people buy products when they buy and how they decide.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
What Is Consumer Behavior?
Consumer behavior is the study of how people buy, use, and think about products and services. This study also covers how they dispose of these items to meet their needs and desires.
It includes many activities and decisions. It starts with the recognition of a need or desire. Then, there is the search for information and the evaluation of options. After that, sales takes place, followed by post-sales evaluation. Finally, the process ends with the disposal of the product or service.
Why Is Consumer Behavior Important?
Understanding consumer behavior is a crucial component of any successful business strategy. This field has many facets. It explains why, when, how, and where people spend their money. It offers valuable insights for businesses to connect with customers in a better way.
Some important factors influence consumer behavior like:
Cultural Factors: Cultural factors are essential. They shape a consumer’s wants, behavior, and attitudes. They do this through family, society, and education.
Social Factors: Peers, groups, and social roles influence purchasing decisions a lot.
Psychological Factors: Psychological factors are individual motivators. They include perception, beliefs, and attitudes. They affect buying behavior.
Personal Factors: Personal factors shape the consumer experience. These factors include age, job, lifestyle, and economic status.
Theodore Levitt said, “People don’t want to buy a quarter-inch drill. They want a quarter-inch hole!” This is the key to understanding consumer behavior. It’s about grasping their basic needs and desires.
Models of Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior models generally fall into two categories:
- Traditional and
- Contemporary.
Traditional Models Of Consumer Behavior
Traditional models are older theories. These models developed when markets were less complex. These models are the foundation for modern understanding of consumer behavior.
They include:
Learning Model of Consumer Behavior
This Model of Consumer Behavior says your customers form habits by a process of learning. The customer’s drive to fulfill needs influences this learning. Your customers get information through experience and engagement. You must repeatedly present your product so it becomes familiar and preferred.
Recognizing the learning model means acknowledging something. You can use this as an opportunity. That means every time a customer interacts with your brand, it’s a chance to educate them about your product’s value. So, the key is to focus on educational content and lots of marketing exposure. This affects how you market and engage with your customers.
Starbucks employs the Learning Model through its rewards program. Customers get free drinks and birthday rewards. They also earn stars for each purchase. This system incentivizes repeat visits and boosts loyalty.

This strategy has worked well and has helped boost Starbucks’s revenue.
Psychoanalytical Model of Consumer Behavior
The Psychoanalytical Model of consumer behavior relies on Freudian psychology. It emphasizes how unconscious motives influence your customers’ choices. It also suggests how deep-seated psychological forces shape buying decisions. These forces can include emotions, experiences, and inner conflicts.
Businesses should leverage these emotional and symbolic meanings. They should design marketing strategies that address deep consumer needs. For example, use influencers and celebrities to endorse your products. This helps brands connect with their target audience on a deeper level.
Luxury fashion brands like Chanel and Louis Vuitton use this model. They link their products with exclusivity, sophistication, and social status.
Many see owning a product from these brands as a symbol of success and a marker of social standing. They appeal to the unconscious desires for status and acceptance.
Sociological Model of Consumer Behavior
The Sociological Model of Consumer Behavior is key for your business. It reveals that purchases are not made in a vacuum. Your customers exist within a social setting that helps shape their buying habits. 92% of consumers trust recommendations from friends and family more than ads.
Key Components of this model include:
- Social Influence: People often base their buying decisions on their social circle.
- Cultural Norms: Guide what people buy based on their shared beliefs and value
- Group Dynamics: A consumer’s role and status in a group affect their buying behavior.

An excellent example of a brand that leverages the Sociological Model is Nike. They craft campaigns around the shared values and aspirations of their target audience. For example, they embrace sportsmanship and self-improvement. This approach makes the campaigns resonate on a deeper, more personal level.
Economic Model of Consumer Behavior
This model states that consumers make purchasing decisions based on self-interest. They aim to maximize utility within their budget constraints. It assumes that consumer choices depend on:
- price changes,
- income levels, and
- the joy (utility) of goods and services.
Businesses can use this model to focus on value and cost in their marketing and product plans.
Businesses should communicate clearly, telling customers about their product’s benefits, features, and competitive prices.
Contemporary Models Of Consumer Behavior
Contemporary models consider factors like social influence and psychological processes. These models use modern theories and methods. They often acknowledge that consumer behavior is a mix of various factors. It includes:
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell (EKB) Model of Consumer Behavior
The Engel-Kollat-Blackwell (EKB) Model is a comprehensive framework. It analyzes your customer’s decision-making process. It can break down consumer behavior into reasonable steps. Many internal and external factors influence these steps.
Key Stages of the EKB Model:
- Problem Recognition: Your customer realizes a need or desire to fulfill.
- Information Search: The search for pertinent information to make a decision begins.
- Alternative Evaluation: Your customer assesses different choices available in the market.
- Purchase Decision: They make a final decision on whether to buy and which option to choose.
- Post-Buying Behavior: The customer evaluates the product, influencing after-behavior and brand perception.
Amazon utilizes the EKB Model in a smart way. It offers an extensive online platform that is easy to navigate. The platform also aids in information search and evaluation.

Customers use Amazon for reviews, recommended products, and detailed product descriptions. These help them make informed decisions.
Using the EKB model, you can identify what makes your customers see a problem. You can also see the criteria they care about during the evaluation.
Black-box model (Stimulus-Response Model of Consumer Behavior)
The Black-box model is often called the Stimulus-Response Model. It offers a framework for understanding consumer decision-making from a business perspective. It sees the mind of the consumer as a ‘black box’. Outside factors like marketing and internal factors like beliefs can influence it.
There are two types of stimuli:
- Marketing stimuli: Product, Price, Place, Promotion
- Environmental stimuli: Economic conditions, social factors, and technological changes
Your task is to guide the consumer from stimulus to desired response. This response is usually the sale of a product or service. By studying consumer behavior, you can fine-tune your marketing to trigger positive responses.
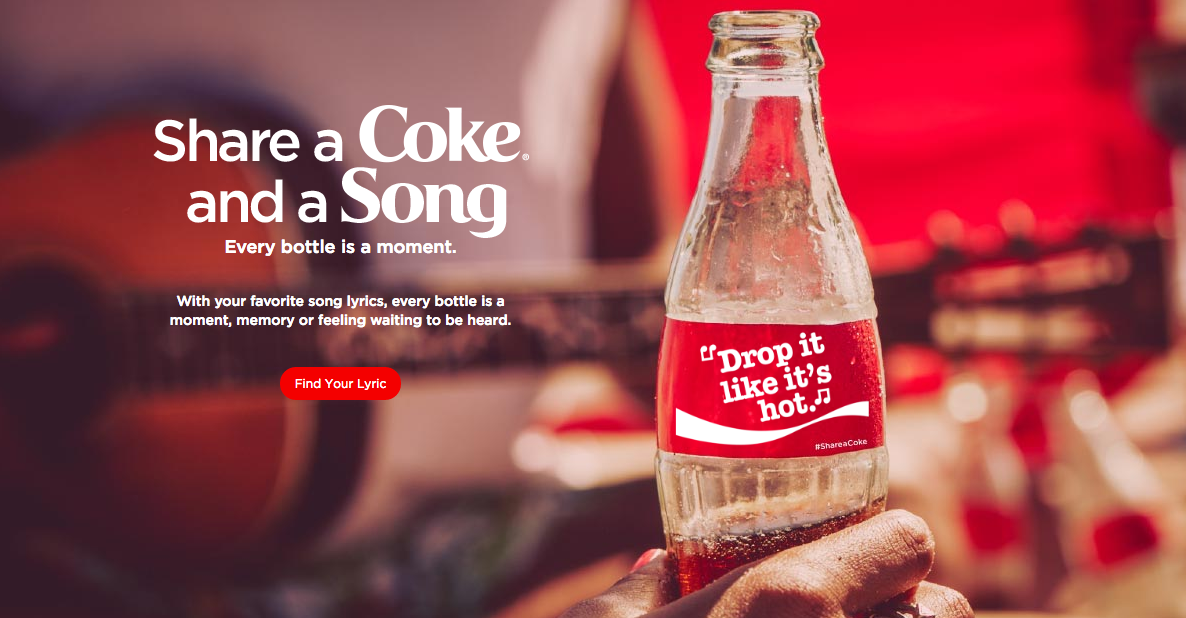
Coca-Cola uses the Black-box Model. It does so in its global marketing campaigns. One such example is the ‘Share a Coke’ campaign. Coca-Cola created universal messages that evoked feelings of happiness, togetherness, and refreshment. This stimulates positive emotions and associations. It leads to more brand recognition and consumption.
The company can keep a strong emotional connection through its stimuli (advertisements). This connection affects consumer responses (purchases) in a direct way.
Hawkins Stern Impulse Buying Model of Consumer Behavior
The Hawkins Stern Impulse Buying Model says that customers make some purchases impulsively. These purchases happen without the usual decision-making process. Impulse buys come from external stimuli and internal states. These can include emotions, rewards, and the immediate appeal of an item.
The model categorizes impulse purchases into types. These include:
- Pure impulse buying: here you just buy something without planning for it
- Reminder impulse buying: here when you see something and remember you need it
- Suggestion impulse buying: when you’re persuaded by ads or displays
- Planned impulse buying: when you intend to buy something but end up buying extra stuff.
Each type depends on certain factors. These factors can be promotional cues to in-store displays and the consumer’s mood.
This model helps you create marketing strategies that can tap into your customers’ impulse buying. You can enhance impulse buying behavior by:
- placing products in a strategic way,
- advertising them with compelling and emotive language, and
- offering limited-time deals.
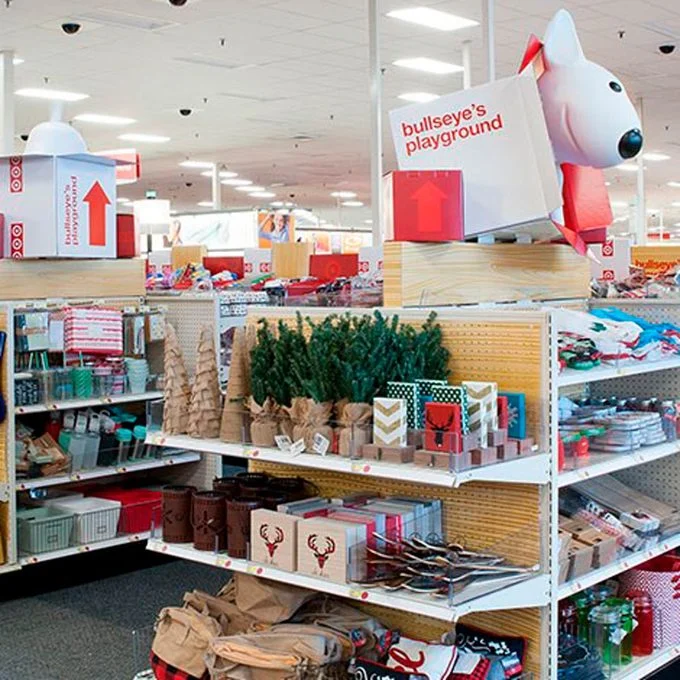

Target is well-known for its effective in-store layouts that encourage impulse buying. Target designs its stores to maximize impulse purchases. It does this by placing enticing items in the “dollar spot” at the store entrance. Additionally, it lines the checkout lanes with tempting products.
Howard Sheth Model of Consumer Behavior
John A. Howard and Jagdish N. Sheth developed the Howard-Sheth Model in the 1960s. It is a theory that aims to explain the complexity of how consumers make decisions. It does this through a series of linked variables.
It distinguishes between three types of decision-making. They are:
- extensive problem-solving
- limited problem-solving
- routinized response behavior
Each varies in consumer involvement and information processing.
The model has inputs from marketing and social sources. It includes the process of how consumers perceive and process information. It covers outputs like purchase decisions and post-purchase behavior. The model also includes the psychological variables that affect these stages. These variables include learning, motives, and attitudes.
By breaking down each variable, your business can tailor its methods. This ensures that your messages resonate with your audience. It happens at every stage of their buying journey. It helps you understand the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind consumer decisions. This lets you optimize your business automation strategies well.
Nicosia Model of Consumer Behavior
Francesco Nicosia developed the Nicosia Model in the 1960s. It focuses on the circular and interactive process between a brand and its consumers. The model has four major fields.
- Firm’s attributes and how it communicates to consumers
- Consumer’s attitudes and actions
- Consumer’s search and evaluation
- Feedback from the consumer
The Nicosia Model helps businesses make clear, targeted marketing messages. They use it to communicate the product’s value to the right audience. Also, it emphasizes feedback. Feedback refines and customizes future marketing messages. This makes it a crucial tool for building strong consumer relationships.
Webster and Wind Model of Consumer Behavior
Frederick E. Webster Jr. and Yoram Wind developed the Webster and Wind Model. They developed it to understand the organizational buying process. It identifies four sets of variables that influence buying decisions within organizations:
- Environmental Variables: External factors such as market conditions, competition, and regulatory policies.
- Organizational Variables: Structure, technology, and objectives within the buying organization.
- Interpersonal Variables: Interactions and relationships among members of the buying center.
- Individual Variables: Personal characteristics and criteria of the decision-makers.
Understanding these variables allows businesses to tailor their approach when targeting potential clients. Businesses need to understand the client’s environment and organizational structure. It helps them to adjust their product or services to the client’s context. Also, understanding how people interact and what each person wants helps businesses talk and negotiate with them in a way that works.
Sheth Family Decision Making Model of Consumer Behavior
Jagdish N. Sheth and his colleagues proposed the Sheth Family Decision-Making Model. It underscores the complexity of purchase decisions made by families rather than individuals. As per the model, within a family, different members may play various roles in the decision-making process, such as
- information gatherer,
- influencer,
- decision-maker,
- purchaser, and
- user.
It also considers factors such as family life cycle, role structures, and conflict resolution methods. This can impact the family’s purchasing decisions. The model is relevant for highly involving products and services that benefit family members.
IKEA uses this model. They create store layouts and ads that appeal to both adults and children.
This encourages family visits to their stores and impacts the collective decision-making process. The store focuses on experiences that effectively prompt purchases from multiple family members.
Pavlovian Model of Consumer Behavior
The Pavlovian Model applies the ideas of classical conditioning to consumer behavior. This suggests that consumers learn by linking things through repeated exposure. In this context, a brand or product is a neutral stimulus. It becomes linked with an emotional or psychological response, an unconditioned stimulus. This happens through repeated pairings. Eventually, the brand or product causes a conditioned response, a purchase decision.
This model shows the power of branding, advertising, and repetition in shaping consumer preferences and buying behaviors. Businesses can use thematic ads that evoke emotions or values in line with the brand’s image. This can foster a strong mental link between the stimuli and the response.

McDonald’s uses jingles and the iconic golden arches in its branding. This helps McDonald to create strong mental brand associations.
What pops up in their minds when consumers see the logo or hear the jingle? Of course, they immediately think of the taste of the food and the dining experience. These sensory cues trigger cravings and positive emotions, encouraging repeat visits.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory of Consumer Behavior
Abraham Maslow’s theory proposes a five-tier model of human needs. These needs are depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. From the bottom up, these levels are:
- physiological needs (food, water, warmth, rest),
- safety needs (security, safety),
- belongingness and love needs (intimate relationships, friends),
- esteem needs (prestige and feeling of accomplishment), and finally,
- self-actualization needs (achieving one’s potential, including creative activities).
Maslow’s theory suggests that products and services fulfill specific needs. These needs can be marketed according to their place in Maslow’s hierarchy. You can create messages that meet your target audience’s emotional and psychological needs. This goes beyond functional benefits, allowing you to connect on a deeper level.
Final Words
By analyzing consumer behavior models, businesses can predict market behavior. This helps craft strategies that appeal to customers’ needs. Aligning marketing strategies with consumer behavior improves satisfaction. It also boosts efficiency in targeting through personalized ads and product development. Additionally, it ads in predicting future trends, allowing for better planning.
Studying consumer behavior models provides deep insights. These insights help understand market patterns. They are crucial for building lasting customer relationships. This gives businesses the power to connect, influence, and inspire consumers. Ultimately, using these insights benefits both business and customers, driving growth and loyalty.
Author

Aryan Jalan, a professional SEO consultant boasting five years of expertise, is dedicated to driving marketing success for businesses. An avid learner, he blends work with leisure, exploring books and new destinations.








Leave a Reply